What Students in Medical Lab Technician Training Should Know about the Anatomy and Physiology of Blood
August 16, 2019
Blood is thicker than water—literally and figuratively. It also does a lot for our bodies. Blood gives us oxygen, nutrients, helps fight infection and illness, and helps remove waste. Additionally, blood helps our organs function and the body regulate pH levels and body temperature. In other words, blood is one of the human body’s most vital components.
We’re all aware of how important blood is to our everyday functioning, but you may have never actually thought about how blood works. Since blood testing is a major part of studying to become a medical lab technician, here are a few things you need to know about the anatomy and physiology of blood.
Blood Comes Together Through Four Types of Blood Cells
The average human has more than five litres of blood in their system, which makes up around eight per cent of our body weight. Blood cells also comprise half of blood’s overall volume, and blood is made of four major components: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
Red blood cells (aka erythrocytes) bring nutrients and oxygen to tissues, and make up 45 per cent of blood’s total contents. White blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets (thrombocytes) only make up less than two per cent of blood, but they still play important roles. The former is the immune system’s cells, and are used to fight infections, while the latter are cells that form clots to help wounds heal. Plasma is the yellow fluid component of the blood, comprising more than half of its volume. It contains numerous proteins and nutrients, as well as glucose, hormones, water, waste, and gases.
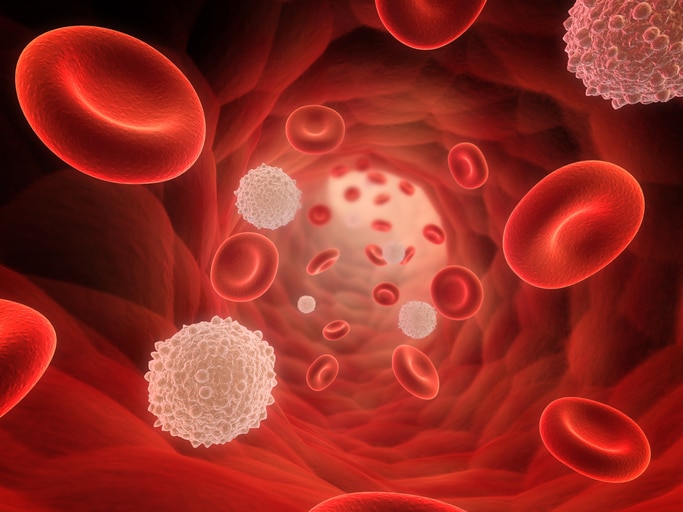
Red and white blood cells are only two components of what helps makes up blood volume
Plasma is Also Divided into Three Different Categories of Proteins
Although 92 per cent of plasma is comprised of water, almost all of the remaining eight per cent is made of three classes of proteins. Students in a medical laboratory technician program may be interested to know that the most prominent of these is albumin, which draws water from tissue and brings it into the bloodstream, helping maintain the regulation and balance of osmosis.
Second to this are globulins, which are molecules that transport substances throughout the blood stream, respond to foreign agents like viruses and bacteria, and inhibit enzymes. Lastly, the least prominent of these proteins is fibrinogen, a protein produced by the liver which helps to form blood clots and heal wounds.
Students in Medix College’s medical lab technician program will learn how to collect blood samples
Those in a Medical Lab Technician Course Should Understand the Importance of Blood’s Regulation
During your medical lab technician training, you’ll learn about how heart activity works, as well as collecting patients’ blood and tissue samples in the labs. It’s worth remembering that the heart’s blood pressure is proportionate to the body’s blood volume, and that blood needs to be regulated enough to achieve homeostasis.
Both blood pressure and volume needs to reach a high enough level so that blood can be delivered to all tissues. This process is known as tissue perfusion. Moreover, blood volume needs to remain at a stable, healthy level, as too little can send the body into hypovolemic shock, while too much can lead to heart failure, aneurysms, coronary artery disease, and hypertension. During your training, you’ll learn more about the functions of the major organ systems and how to assist in identifying common pathologies.
Looking to enrol in a medical lab technician course?
Contact Medix to find out more.



